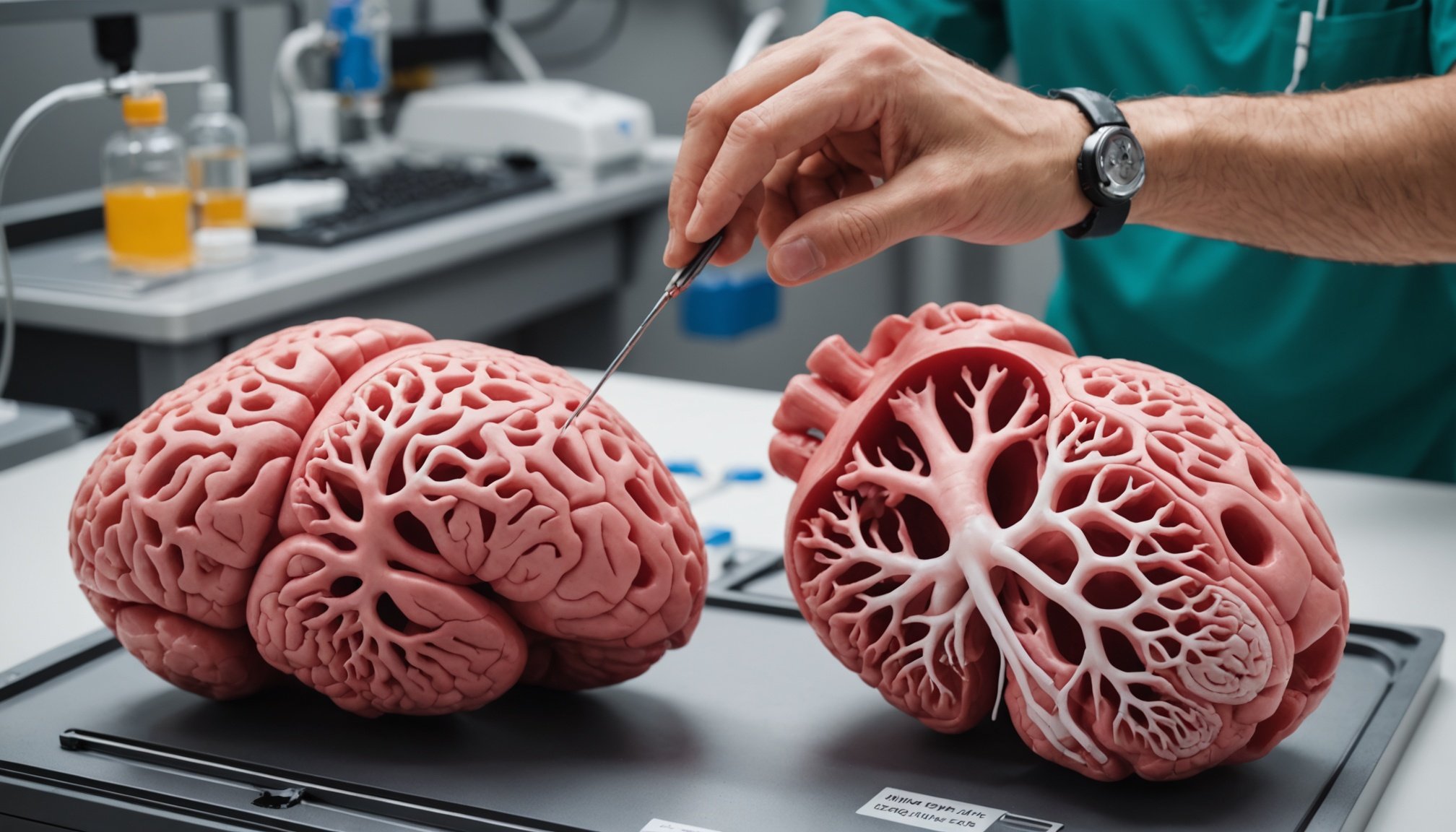
Current Applications of 3D Printed Organs in Medical Training
3D printed organs are rapidly transforming the landscape of medical training applications. By simulating real human anatomy, these models enable medical professionals to gain hands-on experience without the ethical concerns associated with cadavers.
Modern technologies in 3D printing have progressed to a point where organs are not only anatomically accurate but also realistic in texture and functionality. The precision in replicating complex structures makes simulation training more effective and engaging. This innovation has proven particularly valuable in surgical training, allowing trainees to practise procedures repeatedly until they master them.
Also read : Exploring Phage Therapy: A Promising Answer to Combat Multi-Drug Resistant Bacterial Infections
Interesting case studies showcase the integration of 3D printed organs into medical curricula. For instance, a renowned medical school in the UK uses these models to teach cardiac surgery, resulting in a 30% improvement in student performance. These success stories underline the effectiveness of adopting such advanced simulation training tools, encouraging other institutions to follow suit.
When comparing 3D printed organs to traditional models, the former offers superior customisability and adaptability. Unlike traditional methods that use formaldehyde-preserved specimens, 3D models eliminate health hazards and provide a more sustainable alternative. 3D printed organs thus stand as a revolutionary step in advancing modern medical training.
Topic to read : Exploring the Impact of Mindfulness Meditation on Alleviating Generalized Anxiety Disorder Symptoms
Benefits of 3D Printed Organs for Medical Professionals
3D printed organs offer significant advantages in enhancing the medical field. Medical professionals gain improved hands-on experience with these realistic models, enabling them to better understand complex anatomical structures. This tangible interaction aids in refining their diagnostic skills and surgical precision.
One prominent advantage of 3D printing is the opportunity it provides for skills enhancement. Medical professionals can practice and perfect their techniques on detailed replicas of human organs before performing live surgeries. This can translate into more accurate and efficient surgeries, minimising the risks associated with real-life procedures.
Furthermore, 3D printed organs play a crucial role in contributing to better patient outcomes. By allowing for precise pre-surgical planning and practice, these models help ensure that surgeries are performed with utmost accuracy. Moreover, medical personnel can enhance patient safety by reducing unexpected complications during surgery. This results in shorter operation times and faster recovery periods for patients, directly impacting their overall health positively.
In summary, 3D printed organs offer the tools for medical professionals to elevate their expertise while simultaneously improving patient care standards. This fusion of technology and healthcare presents an exciting frontier for medical advancements.
Future Possibilities and Advancements in 3D Printed Organ Technology
The future of 3D printing in the medical field is rich with potential. Pioneering advancements have introduced novel technologies and materials, heralding a new era in medicine. Emerging techniques are leveraging biocompatible materials that mimic the complex architecture of human tissues. This promises to revolutionize transplantation and even drug testing processes.
In parallel, the landscape of advanced medical training is evolving. With the integration of 3D printed organs into curriculums, hands-on experience is more accessible than ever before. These realistic models offer budding surgeons and medical practitioners an unparalleled platform for practice and experimentation, reducing the dependency on live tissues and cadavers.
Technological innovations continue to transform this domain. One exciting prospect is the integration of virtual reality (VR) and artificial intelligence (AI) with 3D printed organs. This combination could allow for real-time simulations and customized training scenarios, elevating the learning experience. AI could also enhance the design and functionality of the printed organs, ensuring they meet specific patient needs more precisely.
These technological innovations not only hold the promise for improved medical outcomes but also offer a glimpse into a future where healthcare training is more immersive and effective.
Expert Opinions and Insights on 3D Printing in Medical Training
Delving into cutting-edge advancements, expert insights reveal transformative potential in medical training through 3D printing. Pioneers in this field highlight significant industry perspectives, suggesting that 3D-printed organs can revolutionise healthcare education. Surveys with industry leaders point to enhanced access to realistic anatomical models, which enable medical students to hone skills in a practical, risk-free environment.
Industry Perspectives
Leaders in 3D printing technology advocate for its role in personalised learning experiences, emphasising the adaptability of printed models to individual patient scenarios. Such perspectives underscore future trends where printed models could serve as essential tools for both practice and assessment within medical curricula.
Long-term Impact
In terms of long-term impact, experts anticipate that 3D printing will bridge gaps in training, offering affordable, replicable, and precise simulations. Furthermore, the ability to practice on diverse anatomical variations closely aligns with ongoing efforts to improve healthcare outcomes and education efficiency.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
Regulatory bodies are currently examining frameworks to manage the use of 3D printing technology. Ethical debates surface around intellectual property rights, as well as the potential commercialisation of printed organs. As future trends evolve, balancing innovation with ethical and legal measures remains paramount.
Visual Aids and Case Studies Enhancing Understanding
The use of visual learning aids in educational settings, particularly in medical education, is immensely valuable. These aids can significantly improve comprehension and retention of complex topics. One example is the use of 3D printed models in teaching anatomy or surgical procedures. These models provide a tangible representation, making it easier for students to grasp intricate details that may be challenging to understand through text alone.
Case study illustrations serve as another powerful tool. They enable learners to apply theoretical knowledge in practical scenarios, facilitating a deeper understanding of concepts. For instance, in studying patient treatment plans, detailed case studies allow students to explore real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills.
When considering integration into training programs, it’s crucial to choose educational tools that cater to diverse learning styles. Incorporating a mix of visuals, such as diagrams, videos, and 3D models, alongside traditional methods, enriches the learning experience. Programs should regularly evaluate the effectiveness of these tools to ensure they meet educational objectives and adapt them as needed to align with evolving educational practices.